![]() Spanish
Spanish ![]() Dutch
Dutch ![]() French
French ![]() German
German ![]() Norwegian Bokmål
Norwegian Bokmål ![]() Polish
Polish ![]() Swedish
Swedish
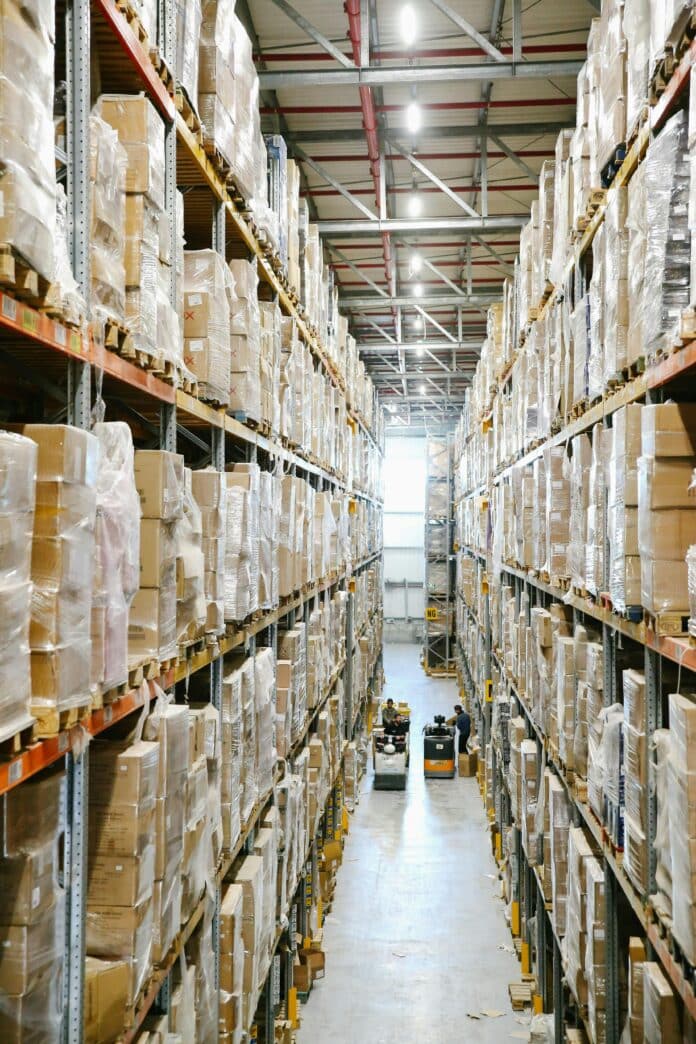
Streamlined and effective procurement management is fast becoming an integral part of organizational success in the modern business world. Most innovative, modern procurement system solutions have turned around the purchasing processes making them very effective and transparent throughout the supply chain.
This guide discusses the basic practices that can facilitate organizations in making their procurement operations more efficient while delivering maximum value against possible risks.
- Understanding the New Procurement Landscape
Digitalization has changed the path of how organizations procure. Paper-based systems now have morphed into integrated procurement system platforms that combine roles into a single solution. These platforms usually give an all-inclusive procurement from vendor management through purchase order processing, all in a much more efficient and transparent manner.
- Strategizing and Setting Goals
Organizations should, before implementing any procurement solution, have clearly defined goals and strategies. That involves diagnosing current procurement headaches; identifying possible ways of improvement, as well as measurable targets. Thought out well, the strategy should align with the organization’s goals but bring factors such as cost savings, process efficiency, and vendor relationship management into consideration.
- Standardization of Procurement Processes
Standardization forms the foundation of effective procurement system management. Procedures should be developed and documented for all procurement activities between requisition and payment. All templates for documentation, approval workflows, and well-defined roles and responsibilities for all stakeholders in the process must be documented.
- Management of Vendors and Relationship Building
Procurement vendor relationships are critical in procurement. All-round implementation of vendor evaluation and management programs such as performance and problem-solving through communication and other aspects will do magic for a procurement enterprise. The essence of these good relationships helps in building better pricing, quality service delivery, and trust.
- Technology Integration and Automation
With recent procurement solutions, technology is used to automate mundane tasks and simplify complicated processes. When evaluating RFP software and other procurement tools, firms should select solutions integrating seamlessly with their existing systems, having user-friendly interfaces and strong reporting capabilities. Using the appropriate technology truly reduces time and effort in manual handling while increasing accuracy and compliance.
- Data Analytics and Performance Monitoring
Effective management of procurement system relies heavily on data-backed decision-making processes. Therefore, organizations must develop strong analytics to track KPIs, monitor spending patterns, and identify optimization opportunities. Further, continuous evaluation of procurement-related data can reveal trends, forecast future needs, and thus enable strategic decisions.
- Risk Management and Compliance
A comprehensive risk management framework is essential for protecting the interests of the organization. This implementation of risk management controls ensures compliance with all applicable regulations, documentation, and auditability of procurement activities expeditiously. Additionally, identifying contingency plans associated with possible risks impacting either supply chain disruptions or vendor issues is critical for any organization.
- Training and Skill Development
The success of procurement system management is primarily dependent on the people who comprise the procurement team. Organizations must provide continuous training so that their personnel are kept current with respect to best practices, new technologies, and changes in market conditions.
This includes technical training on the procurement system employed, and also training in softer skills that would allow for repairs in negotiations and management of vendor relationships.
- Cost Control and Budget Management
Managing costs effectively remains the ultimate goal of procurements. Organizations should have stringent budgeting processes, frequent cost analysis, and stringent means of control over spending. It entails establishing limit approvals and tracking purchasing behaviour with a view to discovering potential cost savings via bulk buying or vendor consolidation.
- Document Management and Record Keeping
Good document and record management is essential to maintaining and auditing compliance. Efficient document management systems should be set up to enable easy storage retrieval and tracking of procurement documents. It pertains to purchase orders, contracts, vendor communications, and so on.
- Sustainable Procurement Practices
To incorporate sustainability in the field of procurement, decision-making regarding product and service procurement should include such evaluation criteria. The suppliers’ supply of goods and services to the organization must also be considered. For instance, this requires having an environmental and social responsibility criterion to screen potential supply partners; this may include how adopting green purchasing policies or strategies will affect the procurement process in the long run among others.
A sustainable procurement system is such a solid benefit to the environment that it could make everything better, cheaper, and more brand-aware.
- Contract Management and Negotiation
Contract management should therefore be effective and especially operational for favourable supplier relationship value delivery by an organization. Strong contract negotiation skills should be developed in an organization and coupled with a process of regularly reviewing contracts, which should further be managed in a dynamically built contract the prime ingredients to ensure continued relevance and value to the organization for all these agreements.
- Constant Improvement and Innovation
Change in procurement organizations will greatly be tied to how dynamic the new procurement functions would be in application to the business. With this in mind, the focus would be set on regularly reviewing and updating processes involved in procuring goods and services, keeping track of market trends along with incorporating new technologies while remaining open to innovative solutions that could increase efficiencies and effectiveness.
- Emergency and Contingency Planning
Develop robust contingency plans to deal with emergency procurement and supply chain disruptions. This will include identifying alternative suppliers, having emergency procurement processes, and regularly testing the response plan’s effectiveness.
- Performance Metrics and Benchmarking
Only when procurement understands and measures its performance can it realize continuous improvement. Setting performance metrics that are clear will enable the organization to assess procurement functions against industry standards and internal benchmarks. The organization should then be able to track important indicators such as cost-saving achievement, procurement cycle times, performance of suppliers in deliveries, and quality indicators.
Regular benchmarking exercises will also assist in identifying areas where performance fails to reach the set industry standards or within the organization itself.
Conclusion
To be successful in procurement system management, one must adopt an all-encompassing approach that integrates strategic planning, adoption of technology, and solid operational practices. Well-scripted in the best practices, the organization would be more productive while making its procurement operations transparent and resilient to risks.
The trick is to maintain the balance between the efficiency of processes, cost control, and relationship management and remain adaptable to changing market conditions and requirements of the organization.
Image source: Pexels
![]() Spanish
Spanish ![]() Dutch
Dutch ![]() French
French ![]() German
German ![]() Norwegian Bokmål
Norwegian Bokmål ![]() Polish
Polish ![]() Swedish
Swedish